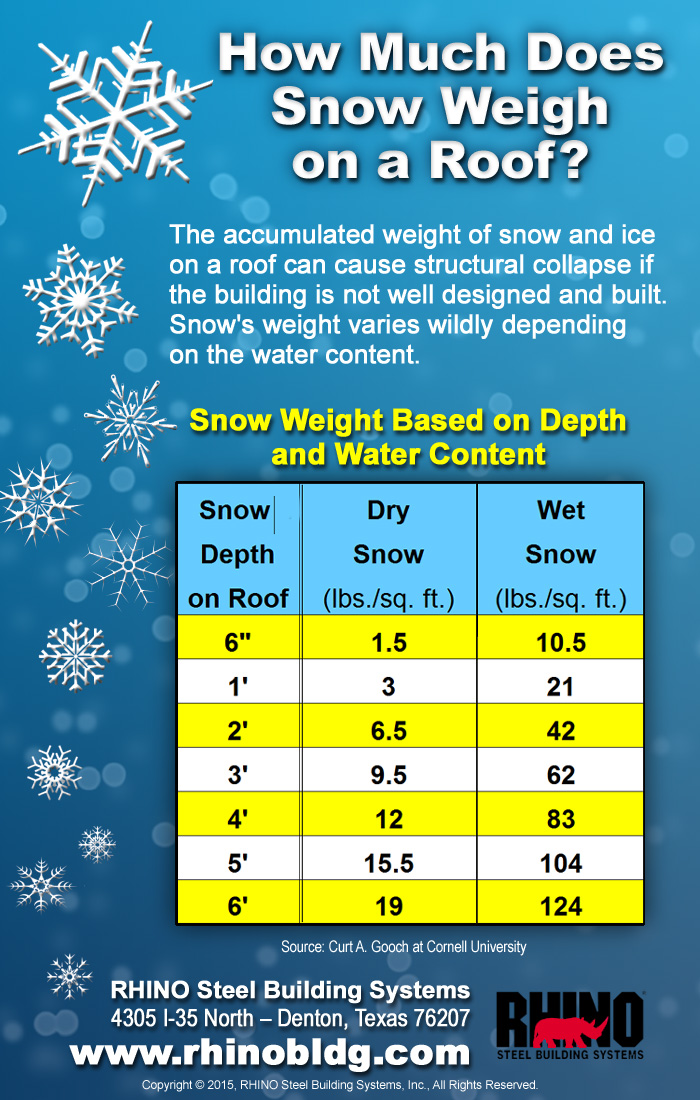
On the other hand snow that stayed on your roof for a few days will settle and while it seems that the cover gets thinner its weight doesn t change it s just the density that is different.
Warm roof types snow load.
Two types of warm roofs that drain water over their eaves shall be capable of sustaining a uniformly distributed load of 2p f on all overhanging portions.
For example fresh snow is soft fluffy and light.
A mountain home should to be able to withstand all that nature throws at it and provide its inhabitants with a warm dry sanctuary from the elements.
Made of a composite material that closely imitates the real thing but with much lighter weight this roofing material provides superior protection for your home and family when it comes to snow and ice.
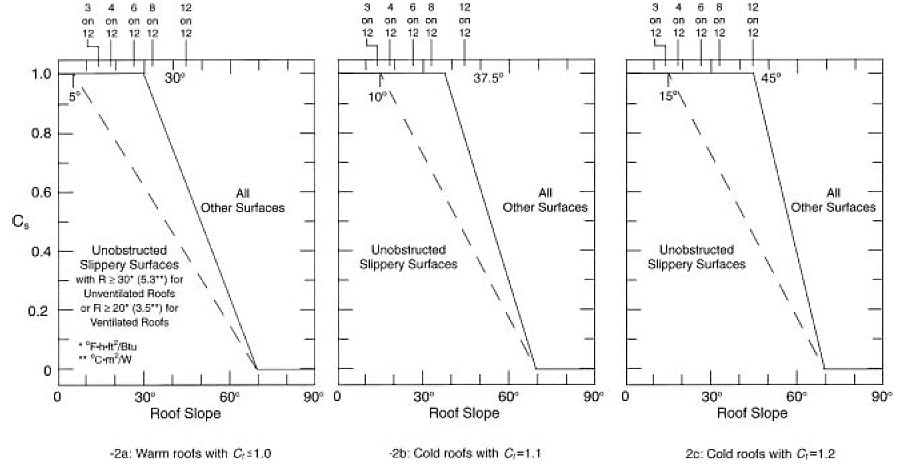
If slope 5 calculate sloped roof snow load.
The easiest way is to push a yardstick into the snow on the roof selecting an area that looks typical of the overall snow depth.
There is no stronger protection against heavy snow loads than shake or slate roofs.
Each state has a listing of building code and applicable guidelines for snow loads as well as details about where the snow load information may be found or purchased.
Use solid line ct 1 1 intermediate roof cs from fig 7 2b slippery unobstructed roof.
2 1 building code definitions.
The purpose of this web site is to provide ground snow load analysis information and data gathered from all 50 states.
If your roof is flat it is more likely to have snow load problems than if it is pitched.
Purpose of this web site.
You need to use a snow load formula for flat roofs.
How snow load can damage your buildings.
Use dashed line ct 1 2 cold roof obstructed roof.
Use dashed line obstructed roof.
Snow and the mountain environment are tough on everything and your home is no exception.
Loads on building structures.
Snow load is the downward force on a building s roof by the weight of accumulated snow and ice.
Those that are unventilated and have an r value less than 30 ft 2 h f btu 5 3 c m 2 w and those that are ventilated and have an r value less than 20 ft 2 h f btu 3 5 cm 2 w.
The density of snow and hence its load per square foot depends on the type of snow.
Tructural engineers use building codes to determine design snow.
That s why it s important to calculate your roof load and be adequately insured for this type of situation.
The amount of additional snow load or surcharge depends on the difference in height of the two adjacent roofs and the lengths of roof perpendicular to the drop in height.
First figure out how deep the snow is piled up there.
Currently the international building.
This chapter contains the building code definitions of snow load types of snow the variables that factor into roof snow loads and the risks various.
Snow can either blown from the low side of the roof towards the high side or is blown off the higher area of the roof onto the lower projected side.