Wind ripples commonly have coarser grains on their crests and this is reflected within wind ripple laminae which show inverse grading coarsening upward slightly within laminae.
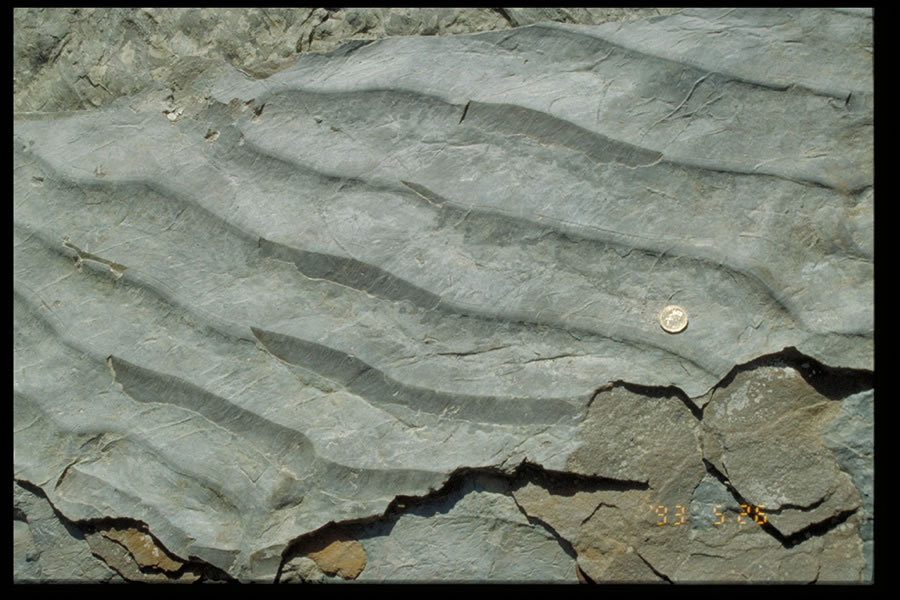
Wave ripple cross lamination.
These wave ripple cross laminations are less clearly symmetric.
Wave ripple cross lamination formed in a sandy lacustrine shoreface in the canadian great lakes is characterized by i small randomly superimposed sets of angle of repose cross lamination with strongly bimodal dips.
Ripples formed by a combination of wave action and unidirectional flow.
Interference ripple sets silurian clam bank formation port au port peninsula nfld.
Wave ripple cross lamination the form of cross lamination see cross stratification produced by the migration of wave generated ripples or combined flow ripples i e.
However the individual ripple cross sections are symmetric characteristic of wave action.
Lensoid and complexly interwoven cross sets.
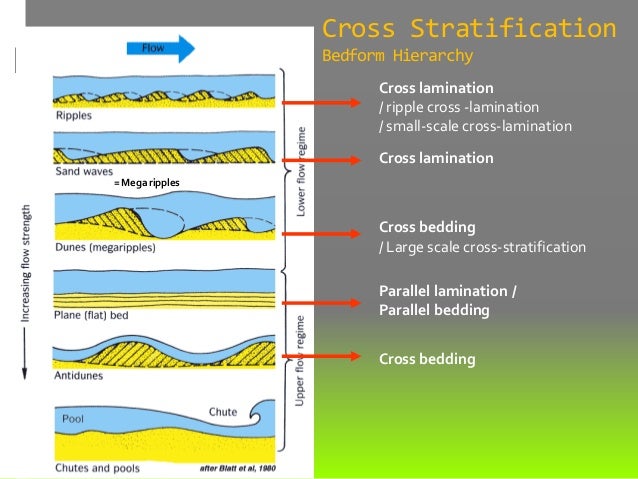
Sections normal to flow may be horizontal defining planar cross lamination 2 d ripples or may be trough shaped defining trough cross lamination 3 d ripples.
Grain avalanches down lee slopes result in small scale cross lamination.
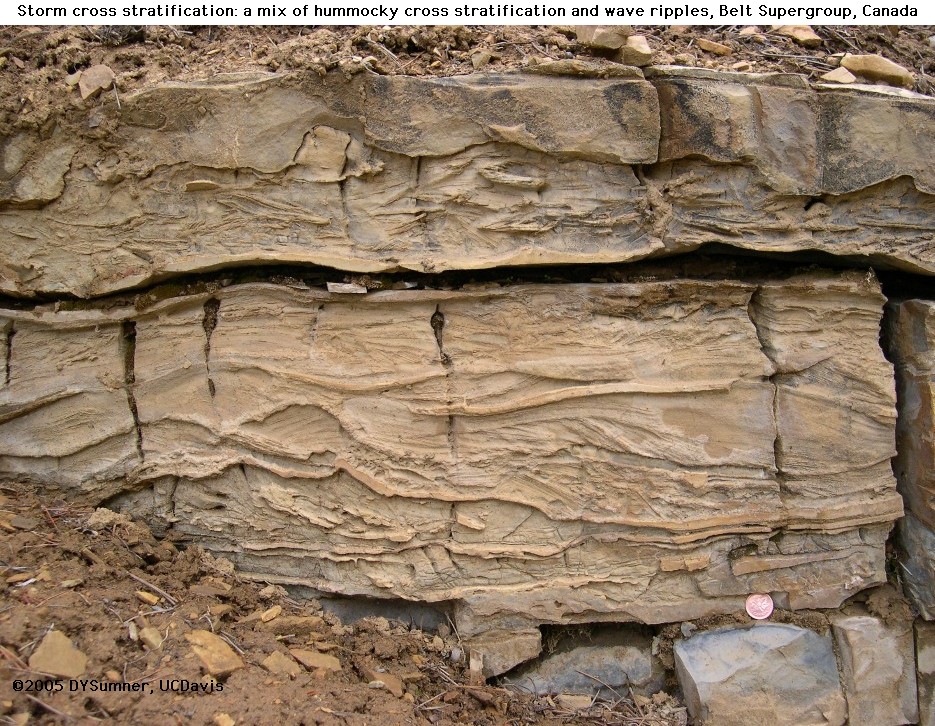
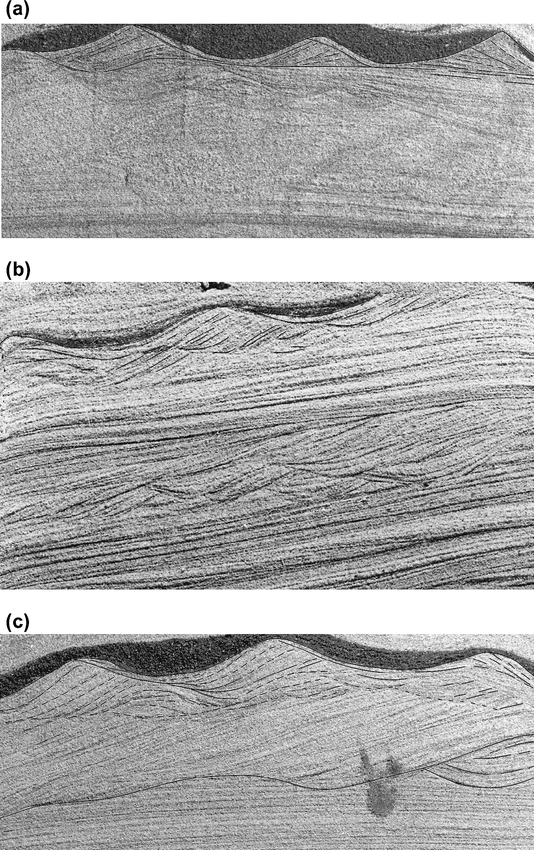
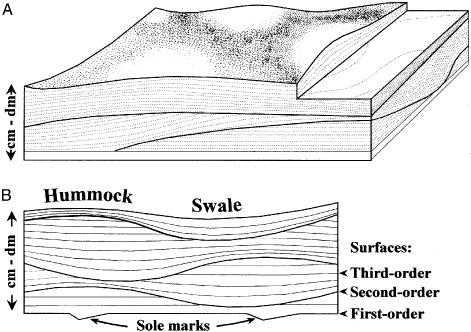
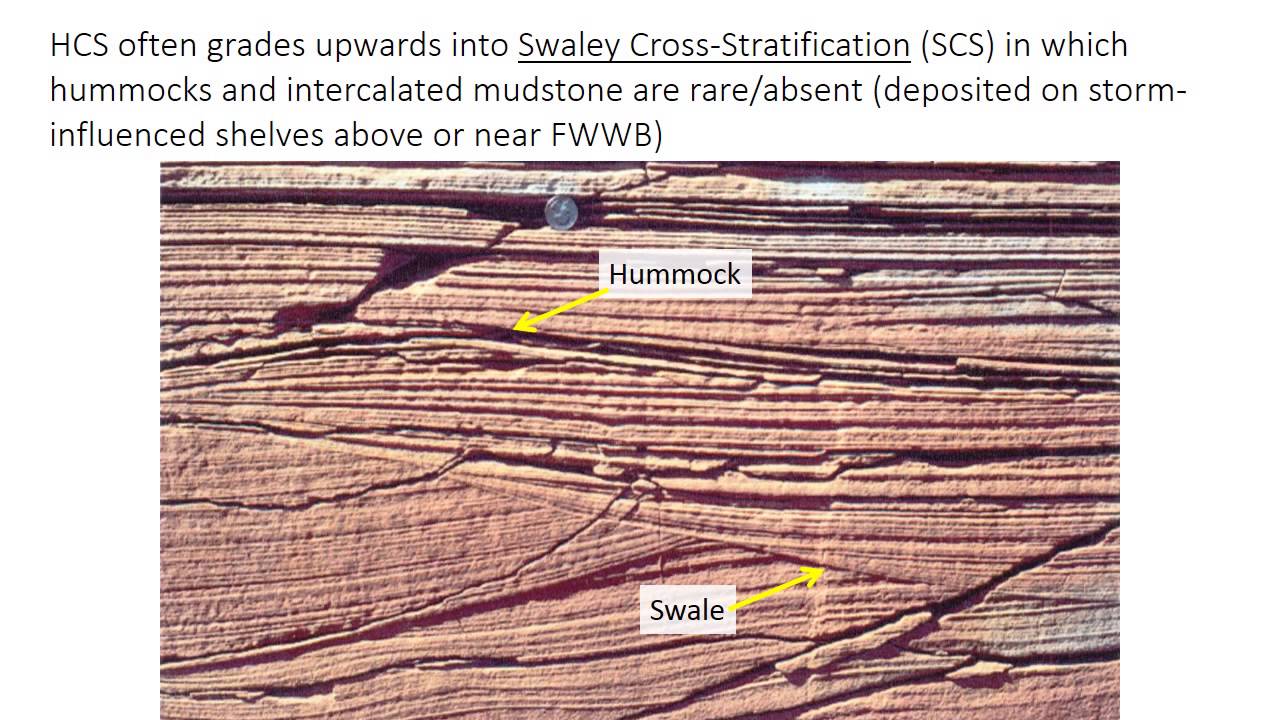
Ancient wave ripple lamination and hummocky cross stratification.
Ancient ripple lamination figure pageindex 22.
Some ripples that may fit this category would be current formed sand waves and storm generated hummocky cross stratification.
The ripples form lateral to one another such that the crests of vertically succeeding laminae are out of phase and appear to be advancing upslope.
Wave ripple cross lamination is characterized by a variety of distinctive features including.
Medium cross lamination are ripples with a height greater than ten centimeters and less than one meter in thickness.
A series of cross laminae are produced by superimposing migrating ripples.
Ripple cross laminae forms when deposition takes place during migration of current or wave ripples.
Ii small superimposed sets of angle of repose cross lamination where the thickest and most prevalent sets have onshore dips and the thinner subsidiary sets dip offshore.
Wind ripple lamination generally comprises thin 1 10 mm parallel laminae defined by slight changes in grain size.